Trustless Attestation
June 01, 2023Using his telescope, Galileo Galilei was the first to discover Saturn’s rings. At the time, he still wasn’t quite sure what they were and wanted to spend more time observing them.
Nonetheless, Galileo knew his discovery was something special and wanted to claim it without giving away any info about it. To do that, he went on to send letters to his friends and colleagues containing “Smaismrmilmepoetaleumibunenugttauiras” which, when unscrambled, becomes “Altissimum planetam tergeminum observavi” meaning – “I have observed the most distant planet to have a triple form.”

Why is Attestation important
As you can see, even centuries ago people had a need to prove time and ownership of a document, discovery, or in modern times even pictures. But our ancestors had to rely on letters not ending up lost, damaged, and the trustworthiness of the receiver. Now we have third-party organisations that handle this for us. And while the message probably won’t be eaten by a horse, you are entrusting data to a third party, which could pose a problem for proving to someone it’s valid.
Let’s say you want to prove the time of taking a picture IMG to person P. If you know ahead of time whom you’re proving IMG to, you can timestamp the picture to a third party you both trust. But what happens if you don’t know who person P is or which the third party it trusts? To ensure your proof is going to be accepted – you will need to send your picture to a lot of “trusted” entities.
“Trust no one on the internet, not even yourself.” - Galileo
Practical use cases
You might be thinking – I’m not Galileo, or for the matter, the majority of people are not astronomers, so why should I care about this?
Car renting
Imagine you rent a car, and after you take the car you notice a minor damaged part which doesn’t prevent you from driving. Let’s say you are in a big hurry, and you can’t return it, but you know that after you ride the car you won’t be able to prove it wasn’t you who did the damage. What you could do is take a picture of the damaged part and post it on the blockchain with . And boom, just like that, now you have proof it happened before you drove the car and can still keep driving it without worries.

Notary services
In many third world countries there are no public notaries to memorise agreed contracts. So what happens? Alice agrees with Bob to sign a contract, but that contract can’t be publicly memorised at that moment. So if Bob changes his mind or wants to forge the contract, it’s very hard for Alice to prove the contract ever happened or that it lost its integrity. But if both persons take a picture with a contract, when the contract is published on a blockchain it’s very hard to invalidate its integrity.

And many more…
There are numerous practical use cases where attestation is important.
Use cases where it’s already being used but can be tremendously improved and optimised with the use of right technology.
Or other use cases, where due to previous technical limitations, a solution just isn’t yet available
- On-chain KYC validation
- DeFi AML validation
- Reputation Systems
- Parking Ticket integrity
- University diplomas
- Passports
- etc.
Building the base
First things first, before building a house, we need to build a good, strong and stable foundation.

Ethereum gave us an abstract base in form of EVM and Smart Contracts and allowed seamless interoperability through a standardised but decentralised machine on top of which we built whole Ecosystems. Important factor was composability through trustlessness, giving us whole bunch of Lego brick to build more complex protocols on top of each other.
The same thing needs to be done for Attestations, bottom up approach. Standardisation of the base layer on how it should be done, but abstract enough to not limit layers on top.
Upon which we’ll build out all the solutions we discussed above.
Ethereum Attestation Service
As per the words in the documentation of EAS
Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS) is a public good that enables anyone to make attestations on or off-chain about anything. You simply register a schema (or use an existing one) about any topic and make attestations using that schema.
How does it work?
EAS (Ethereum Attestation Service) acts as a global registry for creating, verifying and coordinating unique “schemas” used for later attestations.
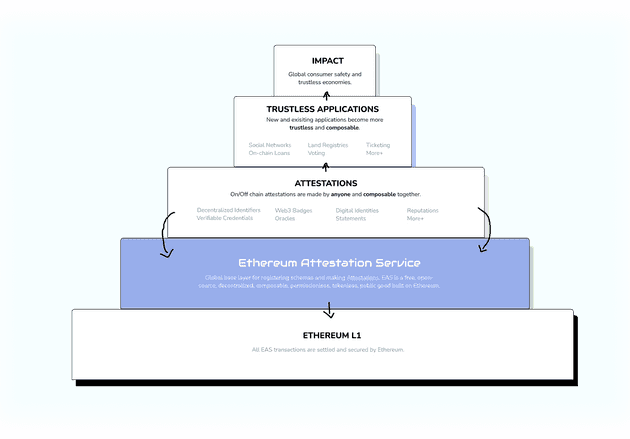
It’s a base layer protocol, written in Solidity and running on EVM compatible chains.
The attestations can work both on-chain and off-chain with different pros and cons depending on the use case that we’re building, we can weight the pros and cons of each option and then decide what’s the best solution for us. Important factor is that it’s not opinionated, so it doesn’t limit us instead of empowering us.
On-chain attestation is going to give a bunch of benefits to applications that need to verify on-the-network, but in return will yield higher prices because of transaction costs and depending on if we use Zero-Knowledge proofs or not, degraded privacy for data that shouldn’t be public.
Off-chain attestation provides value in allowing the entity that is using the service as it’s foundation to have more control over privacy and cost of the product. It isn’t stored directly on-chain but still contains all the necessary attestation data (timestamps, messages, signatures for verification…) but in return, while implementing it, we’ll have to be a bit more careful on how to reduce trust.
Smart Contracts
The protocol’s Blockchain layer can be simplified to having two primary smart contracts written in Solidity.
SchemaRegistry.sol- Smart Contract responsible for registering schemas, later used for creating attestations.EAS.sol- Smart Contract responsible for creating actual attestations on-chain and managing their later state.
So, in a summary:
- One to register a schema
- The other to make instances of those schemas (Attestations)
Pretty simple, but again pretty powerful.

No-Code UI
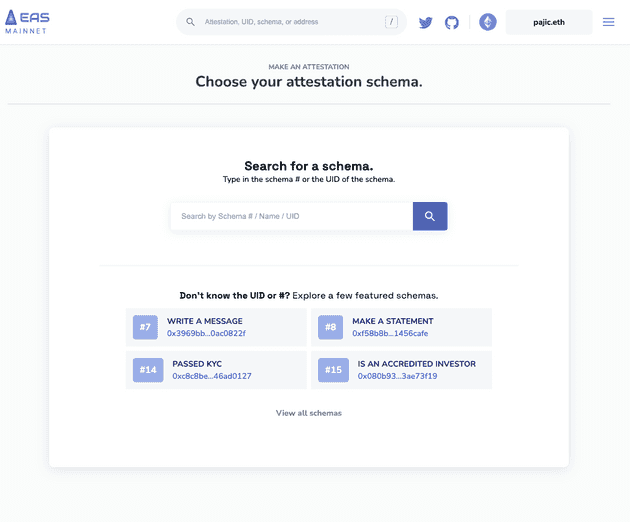
If you don’t want yet to get your hands dirty, you can access the protocol through Its website https://easscan.org/ and start interacting immediately.
- We choose or create a schema, I’ll pick “Write a message” one here 📝
- We make an attestation through a simple form, I’ll claim I’ve discovered Saturn here 🪐
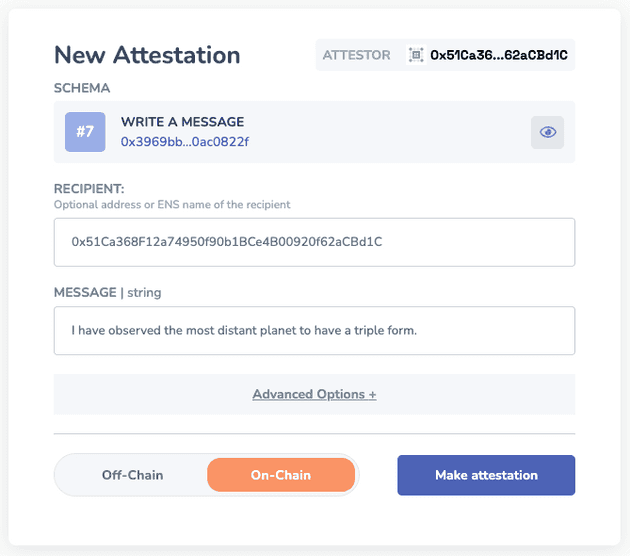
- Confirm the transaction in your Metamask ✅
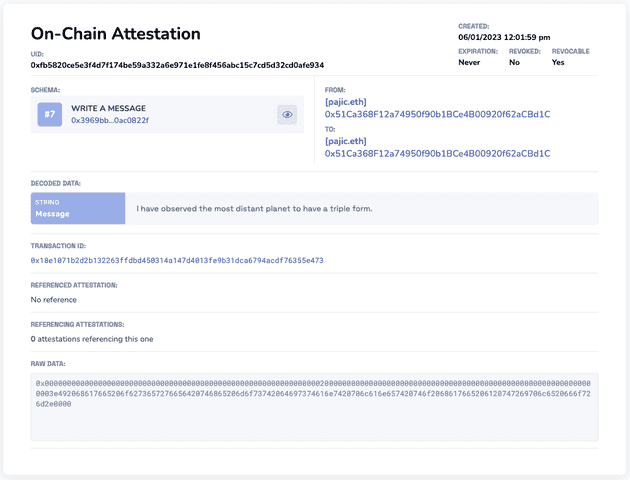
That’s it! In three steps, I’ve claimed some information on-chain in a trustless manner, forever!
My transaction is recorded on Ethereum and I can check the contents of the message in the EAS explorer.
Buidling
It’s exciting to see what other use cases will people come up with. The important thing is that we as a community provide Developers and Builders with good tooling to work with as well as space which encourages and incentivises everyone to do so.
To find out more about Ethereum Attestation Service, you can find protocol’s website here, documentation here and if you want to be more hands one with contributions to the protocol, the Github repo is located here.


